Explain The Process Of Mitosis In A Tissue Culture For Cancer Cells. - Characteristics Of Cancer Cells / When placed on a tissue culture dish, they proliferate until the surface of the dish is covered by a single layer of cells just touching each other.. During mitosis, a eukaryotic cell undergoes a carefully coordinated nuclear division that results in the formation of two genetically identical daughter cells.mitosis itself consists of five active steps, or phases: Most cells in the human body just go about their business on a daily basis in a fairly respectable way let's say that i have some cell here this could be maybe a skin cell or really any cell in any tissue of the body and as it as that tissue is growing or it's replacing dead cells the the cells will experience mitosis and replicate themselves make perfect copies of each other and then those. During mitosis, a cell makes an exact copy of itself and splits into two new cells. Explain the process of mitosis in a tissue culture for cancer cells. Mitosis is the process via which cells divide producing copies of themselves.
Most cells in the human body just go about their business on a daily basis in a fairly respectable way let's say that i have some cell here this could be maybe a skin cell or really any cell in any tissue of the body and as it as that tissue is growing or it's replacing dead cells the the cells will experience mitosis and replicate themselves make perfect copies of each other and then those. Repair of damaged or dead cells. Interphase, when the cell grows and replicates dna in preparation for cell division, and mitosis, during which the actual. Mitosis is the process via which cells divide producing copies of themselves. Mitosis is the process by which genetic matter gets identically replicated many times over.

These cells reproduce by copying their genetic information and undergoing cell division, where the parent cell gives rise to two daughter cells.
Cloning • cloning is the process of producing genetically identical organisms through asexual reproducing, such as budding, binary fission, grafting, stem cuttings and tissue culture. If a cell has plenty of available substrate space, it replicates rapidly and moves freely. Interphase, when the cell grows and replicates dna in preparation for cell division, and mitosis, during which the actual. Cancer cells are taken from a living organism and grown in a culture. This insight will lead to new approaches to disrupt cancers cells' metabolic pathways. Cancer cells do not stop growing when they are touching; The most common form of cell division is called mitosis. During mitosis, a cell makes an exact copy of itself and splits into two new cells. Mitosis, causing the dividing cells to accumulate in metaphase synchronisation of cells in culture cells in tissue culture enter into mitosis randomly. Since cancer is caused by a damage or mutation to cellular dna, mitosis plays an active role in spreading cancer in the body by making exact copies of these damaged and mutated cellular genetic materials. The same division happens during asexual reproduction or vegetative propagation in plants. When placed on a tissue culture dish they proliferate until the surface of the dish is covered by a single layer of cells just touching each other. Explain the process of mitosis in a tissue culture for normal cells.
A short summary of this paper. Prophase, prometaphase, metaphase, anaphase, and telophase. Sweeny kumar in a tissue culture for normal cells, mitosis is a type of cell division in which one cell breaks down to form two identical cells. These cells reproduce by copying their genetic information and undergoing cell division, where the parent cell gives rise to two daughter cells. Most cells in the human body just go about their business on a daily basis in a fairly respectable way let's say that i have some cell here this could be maybe a skin cell or really any cell in any tissue of the body and as it as that tissue is growing or it's replacing dead cells the the cells will experience mitosis and replicate themselves make perfect copies of each other and then those.
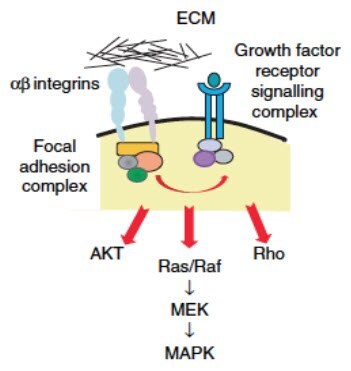
At this point, normal cells will stop replicating.
This phenomenon is called contact inhibition. The difference between normal cells and cancer cells. • tissue culture is the growth of tissues and cells in sterile culture medium. Tissue culture is sometimes referred to as 'sterile culture' or 'in vitro' culture. Cancer cell growth differs from normal cell growth and the number of mitotic divisions are unlimited. Skin cancer type 1 diabetes. The organism would not produce new cells. Since cancer is caused by a damage or mutation to cellular dna, mitosis plays an active role in spreading cancer in the body by making exact copies of these damaged and mutated cellular genetic materials. Cells in tissue culture may be synchronised so that they all enter mitosis simultaneously. Contact inhibition is a regulatory mechanism that functions to keep cells growing into a layer one cell thick (a monolayer). Mitosis is a process cell division, where one cell divides into two identical cells. The organism would not produce new cells. At this point, normal cells will stop replicating.
When placed on a tissue culture dish they proliferate until the surface of the dish is covered by a single layer of cells just touching each other. Mitosis, causing the dividing cells to accumulate in metaphase synchronisation of cells in culture cells in tissue culture enter into mitosis randomly. Cancer cells do not operate in the same way as other cells in the system they occupy, so they replicate and damage surrounding tissues. At this point, normal cells will stop replicating. Mitosis is the process by which genetic matter gets identically replicated many times over.
The same division happens during asexual reproduction or vegetative propagation in plants.
Mitosis, causing the dividing cells to accumulate in metaphase synchronisation of cells in culture cells in tissue culture enter into mitosis randomly. The organism would not produce new cells. Cancer cells do not stop growing when they are touching; Once the surface of the dish is covered, the cells continue to divide, piling up into mounds. Repair of damaged or dead cells. Cancer cells are taken from a living organism and grown in a culture.cancer cells grow at an uncontrolled rate.cancer cells do not stop growing when they are touching; Mitosis is a process cell division, where one cell divides into two identical cells. Figure 4 turn over 18 *18* 0 2. The growth and replication of cells is often described as a cyclic process with two main phases: They continue growing.cancer cells grow multiple layers thick. The difference between normal cells and cancer cells. Learn about organelles and how they perform valuable functions for cellular operation. • plant cells will form undifferentiated callus, but.

0 Komentar